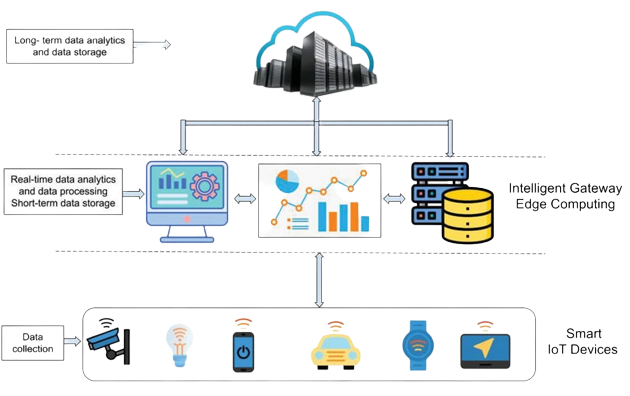
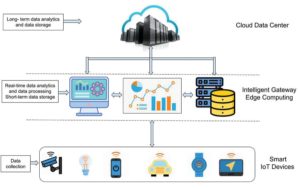
Edge computing refers to the process of processing data closer to the source of its origin. Unlike traditional cloud computing, which centralizes data processing in a few data centers, edge computing distributes data processing across a network of devices, gateways, and servers. In the context of IoT, edge computing involves processing data at the edge of the network, near the devices that generate it.
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized the way devices communicate and operate. With the advent of IoT, the amount of data generated has increased exponentially, leading to new challenges in data processing and management. Edge computing has emerged as a solution to these challenges by enabling decentralized data processing. In this blog post, we’ll explore the role of edge computing in IoT and the benefits and challenges of decentralizing data processing.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing refers to the process of processing data closer to the source of its origin. Unlike traditional cloud computing, which centralizes data processing in a few data centers, edge computing distributes data processing across a network of devices, gateways, and servers. In the context of IoT, edge computing involves processing data at the edge of the network, near the devices that generate it.
Benefits of Edge Computing in IoT
-
Reduced Latency
One of the primary benefits of edge computing is reduced latency. By processing data closer to the source of its origin, edge computing eliminates the need to transmit data to a central data center for processing. This results in faster response times and improved application performance.
-
Improved Reliability
Edge computing also improves the reliability of IoT systems. By decentralizing data processing, edge computing reduces the risk of a single point of failure. In traditional cloud computing, if a data center goes down, it can take down multiple applications and devices. With edge computing, even if a device or server fails, other devices and servers can continue to function.
-
Reduced Bandwidth Costs
Another benefit of edge computing is reduced bandwidth costs. By processing data at the edge of the network, edge computing reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to a central data center for processing. This can lead to significant cost savings in bandwidth costs, especially for IoT devices that generate large amounts of data.
-
Improved Security
Edge computing also improves the security of IoT systems. By processing data closer to the source of its origin, edge computing reduces the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks. Additionally, edge computing allows for the implementation of security measures at the device level, further reducing the risk of security breaches.
Challenges of Edge Computing in IoT
-
Lack of Standards
One of the biggest challenges of edge computing in IoT is the lack of standards. With edge computing, data processing is distributed across a network of devices, gateways, and servers, making it difficult to standardize protocols and communication interfaces. This can lead to interoperability issues and vendor lock-in.
-
Scalability
Another challenge of edge computing in IoT is scalability. As the number of devices and data sources increases, it becomes more challenging to manage and scale edge computing systems. Additionally, the need to maintain and manage a distributed network of devices and servers can be complex and resource-intensive.
-
Data Management
Edge computing also introduces new challenges in data management. With edge computing, data processing is distributed across a network of devices, gateways, and servers, making it difficult to manage and track data. Additionally, edge computing can lead to data fragmentation and duplication, making it challenging to maintain data integrity.
Conclusion
Edge computing has emerged as a promising solution to the challenges posed by the increasing amounts of data generated by IoT devices. By enabling decentralized data processing, edge computing offers several benefits, including reduced latency, improved reliability, reduced bandwidth costs, and improved security. However, edge computing also introduces new challenges, including the lack of standards, scalability, and data management. As IoT continues to grow, edge computing is likely to play an increasingly important role in enabling efficient data processing and enabling new use cases.
To sum up, edge computing offers a viable solution to the challenges posed by IoT data processing. With its ability to reduce latency, increase reliability, and improve security, It can help businesses and organizations unlock the full potential of IoT. However, as with any new technology, it is important to carefully consider the benefits and challenges of edge computing before implementing it in your organization. By doing so, you can ensure that you are making the most of this exciting technology while also managing any potential risks or drawbacks.
Experience the full potential of IoT with Tanbits Edge Computing services. Our expert team can help you reduce latency, increase reliability, and improve security in your IoT data processing. Contact us to learn more about how edge computing can benefit your business